The Psychology Behind Refusing Mental Health Help — And How to Respond

Introduction
Mental health is just as important as physical health, yet seeking help for it is often met with hesitation or outright refusal. Despite the availability of therapists, support groups, and digital resources, many people still reject assistance.
This refusal can be confusing and even frustrating for loved ones who want to help. To respond effectively, it’s essential to understand the psychology behind the refusal; what drives it, why it persists, and how we can gently encourage healthier choices.
Why Do People Refuse Mental Health Help?
There’s no single reason why someone avoids seeking support. Instead, a combination of psychological, cultural, and emotional factors often contributes to this.
Here are the most common reasons:
- Stigma and Shame – Fear of being judged or labeled.
- Denial – Believing “I don’t have a problem.”
- Fear of Change – Worry that treatment will alter their identity.
- Lack of Awareness – Not recognizing the seriousness of symptoms.
- Cultural Beliefs – Family or community norms discourage help-seeking.
- Financial Barriers – Concerns about therapy costs or insurance.
Quote: “Mental health recovery begins with acceptance, but acceptance takes courage.”
The Psychology Behind Refusal
Let’s dive deeper into the mindset and psychological patterns that fuel resistance.
1. Cognitive Dissonance
People often experience a conflict between what they feel and what they believe. For instance, someone may feel overwhelmed but still think, “I should be strong enough to handle this alone.”
2. Defense Mechanisms
Refusal can be a coping strategy. Mechanisms such as denial, avoidance, or rationalization protect individuals from confronting painful truths.
3. Fear of Vulnerability
Opening up to a professional requires trust. Many fear judgment or exposure, leading them to resist support.
4. Past Negative Experiences
A bad encounter with a therapist or healthcare system can make people reluctant to try again.
Common Myths About Mental Health Help
| Myth | Reality |
| “Therapy is only for severe cases.” | Therapy helps with everyday stress, not just crises. |
| “Talking to friends is enough.” | Professional guidance provides structured strategies. |
| “Medication will change my personality.” | Medication balances brain chemistry; it doesn’t erase identity. |
| “If I ignore it, it will go away.” | Untreated mental health conditions often worsen over time. |
Emotional Impact on Loved Ones
When someone refuses help, the emotional toll extends beyond the individual. Family and friends often feel:
- Helplessness – Unsure how to convince them.
- Frustration – Watching a loved one struggle without support.
- Fear – Worrying about potential crises.
- Guilt – Questioning if they could have done more.
This highlights why responding with empathy and strategy is crucial.
How to Respond When Someone Refuses Help
Instead of pushing or lecturing, try approaches grounded in patience, respect, and psychology.
1. Practice Active Listening
- Show genuine interest.
- Reflect their feelings: “I can see this is really hard for you.”
- Avoid judgmental phrases like “You’re overreacting.”
2. Offer Small Steps
Suggest gradual support instead of big commitments:
- Reading an article.
- Joining a casual support group.
- Trying one short therapy session.
3. Normalize the Conversation
Use everyday language:
- Instead of “You need therapy,” say “Talking to someone might make things lighter.”
4. Share Stories and Resources
Hearing about others’ positive experiences can reduce stigma.
👉 You can also explore our guide: When Someone Needs Help but Is Not Willing to Get Help.
5. Respect Boundaries
Pushing too hard may backfire. Respecting autonomy is essential for trust.
Practical Strategies for Encouraging Help
Here’s a step-by-step approach you can apply:
- Start the Conversation – Choose a safe, private setting.
- Use “I” Statements – “I’m worried about you” instead of “You need help.”
- Provide Options – Give choices between therapy, helplines, or online resources.
- Encourage, Don’t Force – Empower them to make their own decision.
- Follow Up – Check in regularly without pressure.
Visualising the Journey of Accepting Help
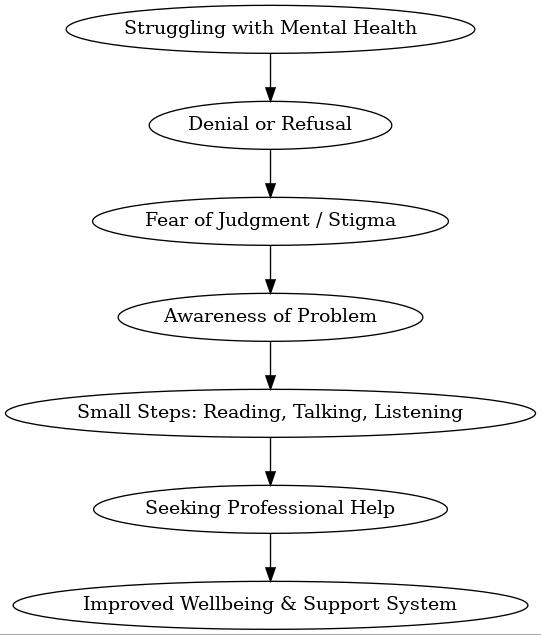
This flowchart shows the gradual progression from refusal to acceptance.
How Wayahead Can Help
At Wayahead, we understand that acceptance is not instant—it’s a journey. Our guides, factsheets, and support resources are designed to make that journey smoother by:
- Providing educational articles on mental health conditions.
- Sharing real-life stories that reduce stigma.
- Offering directories of services so people can find help near them.
- Encouraging support groups for safe, non-judgmental discussions.
Key Takeaways
- Refusal to seek help is often rooted in fear, stigma, and defense mechanisms.
- Responding requires patience, empathy, and step-by-step encouragement.
- Loved ones can play a vital role by listening, normalizing, and providing resources.
- Way Ahead offers accessible tools and information to bridge the gap between refusal and recovery.
Conclusion
Refusing mental health help doesn’t mean someone is beyond support; it means they need understanding, patience, and encouragement in a way that respects their fears and autonomy.
By learning the psychology behind refusal, we can respond better and create a safe environment where seeking help feels natural.
At Wayahead, we believe that every small step toward openness is a big step toward well-being.
Newsletter
Stay up to date
Sign up to our Mind Reader newsletter for monthly mental health news, information and updates.